Introduction
In this document I will be comparing the server
side and client side scripting that takes place in websites when you're using a
web browser. I will explain the positives and drawbacks of each and what they
are generally used for and their purpose.
Client Side Scripting over Server Side Scripting
Client side scripting is when a scripting language
runs its functionality on the user's PC through their web browser rather than
the server running the website. Server side scripting happens where the website
is hosted directly on the server, the opposite of client side scripting. People
who host web servers tend to run the most demanding scripts on the client’s PC,
this is due to the fact that the client’s PC is a much faster system. Since
servers are designed to just run a huge amount of data on the internet, and if
you’re using a shared server design, running scripts on the user’s PC is a huge
advantage.
Client side and server side scripting have
different scripting environments which they run on, obviously client side
scripting is ran on the web browser itself and works with the HTML code. While
server side scripting is designed to run on a web server environment, and
might even use a whole different scripting language altogether.
Client side has a few advantages over server side
scripting, especially for the goal of making interactive web pages and
interactive gadgets or applets. First the system that client side scripting
will be running on is most of the time going to be a lot faster than the
server. This means any client side scripting will run significantly faster than
server side scripting and allows for fast web page loading. It also means the
interactivity will not be hindered, as for server side scripting, it might
actually slowdown interactive elements of the web page.
Server side scripting is mostly used for
communicating with databases and retrieving information on the user. Things
like e-commerce, social networks, security, privacy and data keeping will be
used for server side scripting, as servers can handle huge amounts of data.
Which is where client side scripting can fall short, but since interactivity
and web page presentation does not depend on huge amounts of data, it does not
need that sort of power.
Client side scripting is a lot more advantageous to
use against server side scripting for interactivity of web pages. Simply due to
the fact that the computer running the said script will be faster, which also
in turn relieves a huge amount of stress on the server side scripting. Which
means it allows for the server side scripting to deal with more specific
situations to do with databases and security.
User Experience and Client Side Scripting
Client side
scripting is a huge advantage for basic user experience and interaction with
the web page, it is extremely useful since it is used mainly for interaction
and the design of the web page. User experience in this day and age depends
heavily on the usage of client side scripting, things like drop-down boxes
would not be even possible without the usage of client side scripting.
Before scripting,
things were extremely basic as web sites only used HTML and CSS, there weren’t
any forms or animations of any sort, nor were there any drop-down boxes. Client
side scripting is extremely important because it saves the user time, and makes
your web page easier to navigate, and provides visual benefits in making your
design more appealing and understandable. For example, imagine a website like
Amazon, without drop-down boxes:
As you can see, I
am hovering my mouse over “Shop by Department” that then shows a drop down box
which contains a comprehensive lists of all the different Amazon shopping
departments I can search in. If there was no client-side scripting, this would
either load extremely slowly, or would not exist at all. Since server side
scripting is so slow, it would be more beneficial to have this has a button
that redirected you to a list of different departments if client side scripting
did not exist.
We take for granted
our experience viewing web pages and how helpful a client side scripting
language like a JavaScript aids in the usability of web pages. It’s not only
drop down boxes this would effect either, if you didn’t have client side
scripting, you would not have animated buttons, lists, effects, etc. When JavaScript
did not take off, a lot of interaction
was based around Flash Player by Adobe, but this wasn’t fast or
efficient in making your website fully animated. It could slow down the whole
website for people who did not have fast PCs to run all of the Flash content,
so when JavaScript and client side scripting became an attractive and useful
tool to take advantage of. Websites restructured themselves according to the
use of client side scripting, and has now allowed all of these increased user
experiences.
Even YouTube used
to use Flash Player, and now uses WEBM files to run animated videos, which
takes advantage of client side scripting. The usage of this has also made it
possible to watch videos in sixty frames per second, and up to 4K resolutions,
making the user experience of watching videos in the world wide web much more
enjoyable and hassle free.
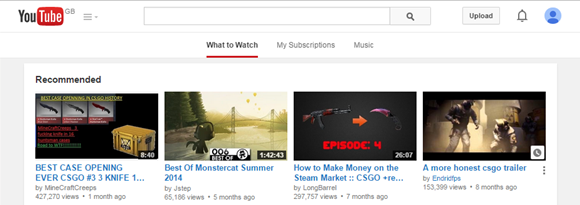
In fact YouTube is
a good example of presenting how client side scripting has aided user
experience and the usability of browsing the web. As you can see in the
navigation bar for watching videos, there are three buttons representing “What
to Watch”, “My Subscriptions” and “Music”. Switching between these is almost
seamless, and it actually loads within the web site itself, rather than your
web browser. Due to pre-loaded client side scripting, if YouTube did not have
client side scripting it probably would not load new pages within itself and
depend much more on the web browser. So like an ordinary website it would
probably redirect you to a different web page stored within a database.
Form Validation and Client Side Scripting
Client side
scripting also forwarded the increase in security on the World Wide Web and has
provided a huge array of benefits for the user. Form validation refers to forms
returning messages based on what the user has inputted into the form’s text
boxes, the form information can even be compared to a database.
However simple
things like checking if a form has actually been filled out or not can be done
on a client side scripting language like JavaScript. A function like this can
be created:
function validateForm() {
var x = document.forms["myForm"]["fname"].value;
if (x == null || x == "") {
alert("Name must be filled out");
return false;
}
}
var x = document.forms["myForm"]["fname"].value;
if (x == null || x == "") {
alert("Name must be filled out");
return false;
}
}
Checking for an
empty form space is a lot faster than checking if the correct information has
been entered because in this function everything is done on the client side.
While correct information has to be compared with a server’s database, or a
database linked to the web server the user is currently using to view the web
site.
Client side
scripting is able improve form validation firstly in the sense that it will
contain the same theme and feel of other client scripting aspects used within
the web page. There will most likely be some aspects that use client side
scripting, and since the form validation will also be using client side
scripting, you can combine these aspects. You could create drop-down select
boxes within the forms, and also make it so it sends and error message if they
chose to ignore the drop-down select box.
Client side
scripting also makes form validation a lot more secure, scripting languages
like JavaScript were designed with security in mind, and it’s extremely
difficult to track information being sent through client side scripting. If you
were to use HTML based form validation, it would be significantly easier for
malicious users to retrieve information if they were to already get past the
first layers of security the website most likely has implemented.
Client side
scripting can also work with server side scripting, which can improve form
validation by a great amount in terms of accurate and valid information. Client
side scripting can work with server side scripting and base information entered
from the client sides form with a server side form, it can also be compared to
the database also. It’s the reason it can sometimes take a long time for you to
log in or to create a new account.
Conclusion:
In conclusion,
client side scripting has improved the user accessibility of the web, and has
enabled people to have a better understanding of the web pages they view. It
has made web pages evolve in the way they look, the way they function and the
way they handle information from a data base. It has also improved the loading
speeds of web pages tremendously over the course of the evolution of client
side scripting. Client side scripting and Server side scripting are both
required for a functioning website, but for interactivity and form validation,
client side scripting is imperative.
Sources:
http://www.w3schools.com/js/js_validation.asp,
02/05/2015, used in page 4 for source code and form validation.
https://www.youtube.com/, 02/05/2015, used
in page 3 for image of the YouTube website.
http://www.amazon.co.uk/ , 02/05/2015, used
in page 2 for image of the Amazon website.
http://www.yourwebskills.com/clientserver.php,
used in page 1 for information gathered.